Categories &
Functions List
- BetaDistribution
- BinomialDistribution
- BirnbaumSaundersDistribution
- BurrDistribution
- ExponentialDistribution
- ExtremeValueDistribution
- GammaDistribution
- GeneralizedExtremeValueDistribution
- GeneralizedParetoDistribution
- HalfNormalDistribution
- InverseGaussianDistribution
- LogisticDistribution
- LoglogisticDistribution
- LognormalDistribution
- LoguniformDistribution
- MultinomialDistribution
- NakagamiDistribution
- NegativeBinomialDistribution
- NormalDistribution
- PiecewiseLinearDistribution
- PoissonDistribution
- RayleighDistribution
- RicianDistribution
- tLocationScaleDistribution
- TriangularDistribution
- UniformDistribution
- WeibullDistribution
- betafit
- betalike
- binofit
- binolike
- bisafit
- bisalike
- burrfit
- burrlike
- evfit
- evlike
- expfit
- explike
- gamfit
- gamlike
- geofit
- gevfit_lmom
- gevfit
- gevlike
- gpfit
- gplike
- gumbelfit
- gumbellike
- hnfit
- hnlike
- invgfit
- invglike
- logifit
- logilike
- loglfit
- logllike
- lognfit
- lognlike
- nakafit
- nakalike
- nbinfit
- nbinlike
- normfit
- normlike
- poissfit
- poisslike
- raylfit
- rayllike
- ricefit
- ricelike
- tlsfit
- tlslike
- unidfit
- unifit
- wblfit
- wbllike
- betacdf
- betainv
- betapdf
- betarnd
- binocdf
- binoinv
- binopdf
- binornd
- bisacdf
- bisainv
- bisapdf
- bisarnd
- burrcdf
- burrinv
- burrpdf
- burrrnd
- bvncdf
- bvtcdf
- cauchycdf
- cauchyinv
- cauchypdf
- cauchyrnd
- chi2cdf
- chi2inv
- chi2pdf
- chi2rnd
- copulacdf
- copulapdf
- copularnd
- evcdf
- evinv
- evpdf
- evrnd
- expcdf
- expinv
- exppdf
- exprnd
- fcdf
- finv
- fpdf
- frnd
- gamcdf
- gaminv
- gampdf
- gamrnd
- geocdf
- geoinv
- geopdf
- geornd
- gevcdf
- gevinv
- gevpdf
- gevrnd
- gpcdf
- gpinv
- gppdf
- gprnd
- gumbelcdf
- gumbelinv
- gumbelpdf
- gumbelrnd
- hncdf
- hninv
- hnpdf
- hnrnd
- hygecdf
- hygeinv
- hygepdf
- hygernd
- invgcdf
- invginv
- invgpdf
- invgrnd
- iwishpdf
- iwishrnd
- jsucdf
- jsupdf
- laplacecdf
- laplaceinv
- laplacepdf
- laplacernd
- logicdf
- logiinv
- logipdf
- logirnd
- loglcdf
- loglinv
- loglpdf
- loglrnd
- logncdf
- logninv
- lognpdf
- lognrnd
- mnpdf
- mnrnd
- mvncdf
- mvnpdf
- mvnrnd
- mvtcdf
- mvtpdf
- mvtrnd
- mvtcdfqmc
- nakacdf
- nakainv
- nakapdf
- nakarnd
- nbincdf
- nbininv
- nbinpdf
- nbinrnd
- ncfcdf
- ncfinv
- ncfpdf
- ncfrnd
- nctcdf
- nctinv
- nctpdf
- nctrnd
- ncx2cdf
- ncx2inv
- ncx2pdf
- ncx2rnd
- normcdf
- norminv
- normpdf
- normrnd
- plcdf
- plinv
- plpdf
- plrnd
- poisscdf
- poissinv
- poisspdf
- poissrnd
- raylcdf
- raylinv
- raylpdf
- raylrnd
- ricecdf
- riceinv
- ricepdf
- ricernd
- tcdf
- tinv
- tpdf
- trnd
- tlscdf
- tlsinv
- tlspdf
- tlsrnd
- tricdf
- triinv
- tripdf
- trirnd
- unidcdf
- unidinv
- unidpdf
- unidrnd
- unifcdf
- unifinv
- unifpdf
- unifrnd
- vmcdf
- vminv
- vmpdf
- vmrnd
- wblcdf
- wblinv
- wblpdf
- wblrnd
- wienrnd
- wishpdf
- wishrnd
- adtest
- anova1
- anova2
- anovan
- bartlett_test
- barttest
- binotest
- chi2gof
- chi2test
- correlation_test
- fishertest
- friedman
- hotelling_t2test
- hotelling_t2test2
- kruskalwallis
- kstest
- kstest2
- levene_test
- manova1
- mcnemar_test
- multcompare
- ranksum
- regression_ftest
- regression_ttest
- runstest
- sampsizepwr
- signrank
- signtest
- tiedrank
- ttest
- ttest2
- vartest
- vartest2
- vartestn
- ztest
- ztest2
Class Definition: TriangularDistribution
statistics: TriangularDistribution
Triangular probability distribution object.
A TriangularDistribution object consists of parameters, a model
description, and sample data for a triangular probability distribution.
The triangular distribution uses the following parameters.
| Parameter | Description | Support |
|---|---|---|
A | Lower limit | |
B | Peak location | |
C | Upper limit |
There are several ways to create a TriangularDistribution object.
- Create a distribution with specified parameter values using the
makedistfunction. - Use the constructor
TriangularDistribution (A, B, C)to create a triangular distribution with specified parameter values A, B, and C.
It is highly recommended to use makedist function to create
probability distribution objects, instead of the constructor.
Further information about the triangular distribution can be found at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triangular_distribution
See also: makedist, tricdf, triinv, tripdf, trirnd, tristat
Source Code: TriangularDistribution
Properties
A scalar value characterizing the lower limit of the
triangular distribution. You can access the A
property using dot name assignment.
Example: 1
## Create a Triangular distribution with default parameters
pd = makedist ("Triangular", "A", 0, "B", 0.5, "C", 1);
## Query parameter 'A' (lower limit)
pd.A
## Set parameter 'A'
pd.A = -1
## Use this to initialize or modify the lower limit parameter of a Triangular
## distribution. The lower limit must be a real scalar less than the upper
## limit C, useful for defining the minimum possible value in scenarios like
## cost estimation or time to completion.
ans = 0
pd =
TriangularDistribution
Triangular distribution
A = -1
B = 0.5
C = 1
|
Example: 2
## Create a Triangular distribution object by calling its constructor
pd = TriangularDistribution (1, 2, 3);
## Query parameter 'A'
pd.A
## This demonstrates direct construction with a specific lower limit,
## useful for modeling bounded data, such as project durations or resource
## requirements.
ans = 1
|
A scalar value characterizing the peak location of the
triangular distribution. You can access the B
property using dot name assignment.
Example: 1
## Create a Triangular distribution with default parameters
pd = makedist ("Triangular", "A", 0, "B", 0.5, "C", 1);
## Query parameter 'B' (peak location)
pd.B
## Set parameter 'B'
pd.B = 0.7
## Use this to initialize or modify the peak location parameter of a Triangular
## distribution. The peak location must be a real scalar between A and C,
## representing the most likely value in applications like risk analysis.
ans = 0.5000
pd =
TriangularDistribution
Triangular distribution
A = 0
B = 0.7
C = 1
|
Example: 2
## Create a Triangular distribution object by calling its constructor
pd = TriangularDistribution (1, 2, 3);
## Query parameter 'B'
pd.B
## This shows how to set the peak location directly via the constructor,
## ideal for modeling the mode of triangularly distributed data, such as
## expected task completion times.
ans = 2
|
A scalar value characterizing the upper limit of the
triangular distribution. You can access the C
property using dot name assignment.
Example: 1
## Create a Triangular distribution with default parameters
pd = makedist ("Triangular", "A", 0, "B", 0.5, "C", 1);
## Query parameter 'C' (upper limit)
pd.C
## Set parameter 'C'
pd.C = 2
## Use this to initialize or modify the upper limit parameter of a Triangular
## distribution. The upper limit must be a real scalar greater than A,
## defining the maximum possible value in scenarios like budgeting or scheduling.
ans = 1
pd =
TriangularDistribution
Triangular distribution
A = 0
B = 0.5
C = 2
|
Example: 2
## Create a Triangular distribution object by calling its constructor
pd = TriangularDistribution (1, 2, 3);
## Query parameter 'C'
pd.C
## This demonstrates setting the upper limit directly via the constructor,
## useful for modeling the maximum bound in applications like cost or time estimates.
ans = 3
|
A character vector specifying the name of the probability distribution object. This property is read-only.
A scalar integer value specifying the number of parameters characterizing the probability distribution. This property is read-only.
A cell array of character vectors with each element containing the name of a distribution parameter. This property is read-only.
A cell array of character vectors with each element containing a short description of a distribution parameter. This property is read-only.
A numeric vector containing the values of the distribution
parameters. This property is read-only. You can change the distribution
parameters by assigning new values to the A, B, and
C properties.
A numeric vector specifying the truncation interval for the
probability distribution. First element contains the lower boundary,
second element contains the upper boundary. This property is read-only.
You can only truncate a probability distribution with the
truncate method.
A logical scalar value specifying whether a probability distribution is truncated or not. This property is read-only.
Methods
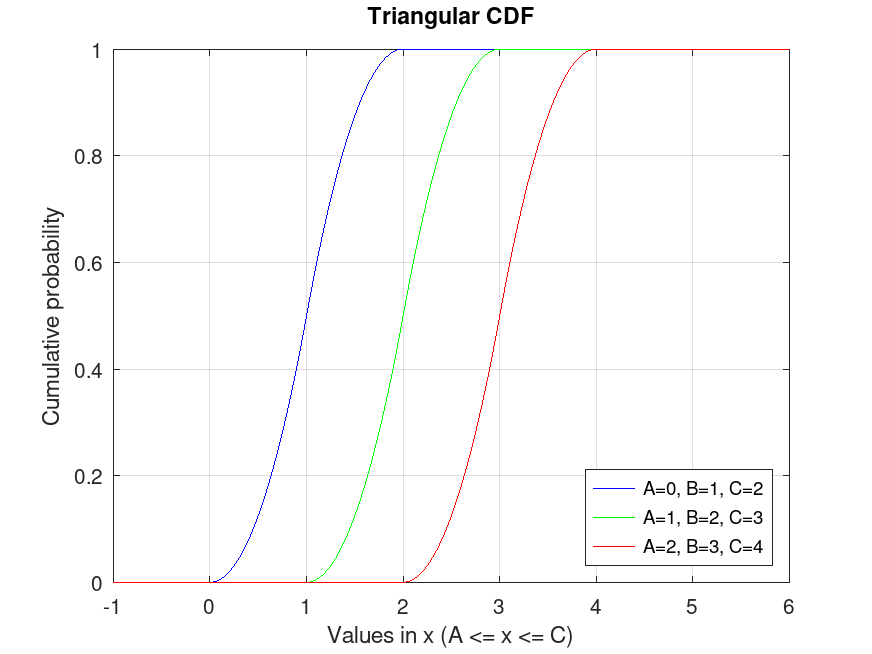
TriangularDistribution: p = cdf (pd, x)
TriangularDistribution: p = cdf (pd, x,
"upper")
p = cdf (pd, x) computes the CDF of the
probability distribution object, pd, evaluated at the values in
x.
p = cdf (…, returns the complement of
the CDF of the probability distribution object, pd, evaluated at
the values in x.
"upper")
Example: 1
## Plot various CDFs from the Triangular distribution
x = -1:0.01:6;
pd1 = TriangularDistribution (0, 1, 2);
pd2 = TriangularDistribution (1, 2, 3);
pd3 = TriangularDistribution (2, 3, 4);
p1 = cdf (pd1, x);
p2 = cdf (pd2, x);
p3 = cdf (pd3, x);
plot (x, p1, "-b", x, p2, "-g", x, p3, "-r")
grid on
legend ({"A=0, B=1, C=2", "A=1, B=2, C=3", "A=2, B=3, C=4"}, ...
"location", "southeast")
title ("Triangular CDF")
xlabel ("Values in x (A <= x <= C)")
ylabel ("Cumulative probability")
## Use this to compute and visualize the cumulative distribution function
## for different Triangular distributions, showing how probability accumulates
## within the bounds, useful in risk assessment or forecasting.
|
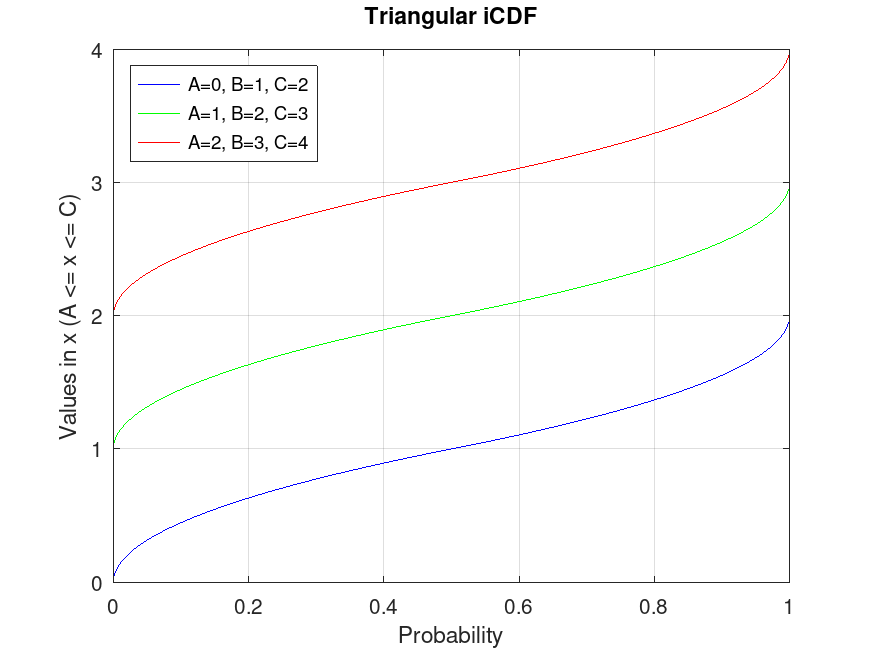
TriangularDistribution: x = icdf (pd, p)
x = icdf (pd, p) computes the quantile (the
inverse of the CDF) of the probability distribution object, pd,
evaluated at the values in p.
Example: 1
## Plot various iCDFs from the Triangular distribution
p = 0.001:0.001:0.999;
pd1 = TriangularDistribution (0, 1, 2);
pd2 = TriangularDistribution (1, 2, 3);
pd3 = TriangularDistribution (2, 3, 4);
x1 = icdf (pd1, p);
x2 = icdf (pd2, p);
x3 = icdf (pd3, p);
plot (p, x1, "-b", p, x2, "-g", p, x3, "-r")
grid on
legend ({"A=0, B=1, C=2", "A=1, B=2, C=3", "A=2, B=3, C=4"}, ...
"location", "northwest")
title ("Triangular iCDF")
xlabel ("Probability")
ylabel ("Values in x (A <= x <= C)")
## This demonstrates the inverse CDF (quantiles) for Triangular distributions,
## useful for finding values corresponding to given probabilities, such as
## thresholds in project planning or quality control.
|
TriangularDistribution: r = iqr (pd)
r = iqr (pd) computes the interquartile range of the
probability distribution object, pd.
Example: 1
## Compute the interquartile range for a Triangular distribution
pd = TriangularDistribution (0, 1, 2);
iqr_value = iqr (pd)
## Use this to calculate the interquartile range, which measures the spread
## of the middle 50% of the distribution, helpful for understanding central
## variability in bounded data like cost estimates.
iqr_value = 0.5858
|
TriangularDistribution: m = mean (pd)
m = mean (pd) computes the mean of the probability
distribution object, pd.
Example: 1
## Compute the mean for different Triangular distributions
pd1 = TriangularDistribution (0, 1, 2);
pd2 = TriangularDistribution (1, 2, 3);
mean1 = mean (pd1)
mean2 = mean (pd2)
## This shows how to compute the expected value for Triangular distributions
## with different parameters, representing the average value in scenarios
## like budgeting or time estimation.
mean1 = 1
mean2 = 2
|
TriangularDistribution: m = median (pd)
m = median (pd) computes the median of the probability
distribution object, pd.
Example: 1
## Compute the median for different Triangular distributions
pd1 = TriangularDistribution (0, 1, 2);
pd2 = TriangularDistribution (1, 2, 3);
median1 = median (pd1)
median2 = median (pd2)
## Use this to find the median value, which splits the distribution into two
## equal probability halves, robust for skewed triangular data in applications
## like scheduling.
median1 = 1
median2 = 2
|
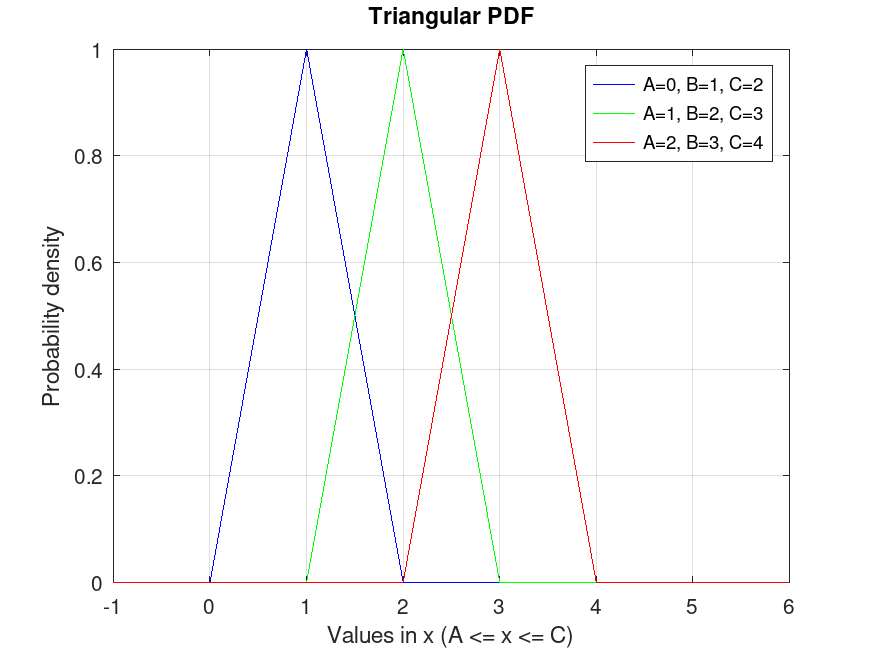
TriangularDistribution: y = pdf (pd, x)
y = pdf (pd, x) computes the PDF of the
probability distribution object, pd, evaluated at the values in
x.
Example: 1
## Plot various PDFs from the Triangular distribution
x = -1:0.01:6;
pd1 = TriangularDistribution (0, 1, 2);
pd2 = TriangularDistribution (1, 2, 3);
pd3 = TriangularDistribution (2, 3, 4);
y1 = pdf (pd1, x);
y2 = pdf (pd2, x);
y3 = pdf (pd3, x);
plot (x, y1, "-b", x, y2, "-g", x, y3, "-r")
grid on
legend ({"A=0, B=1, C=2", "A=1, B=2, C=3", "A=2, B=3, C=4"}, ...
"location", "northeast")
title ("Triangular PDF")
xlabel ("Values in x (A <= x <= C)")
ylabel ("Probability density")
## This visualizes the probability density function for Triangular
## distributions, showing the likelihood within the bounds, useful for
## understanding data distribution in risk analysis.
|
TriangularDistribution: plot (pd)
TriangularDistribution: plot (pd, Name, Value)
TriangularDistribution: h = plot (…)
plot (pd) plots a probability density function (PDF) of the
probability distribution object pd.
plot (pd, Name, Value) specifies additional
options with the Name-Value pair arguments listed below.
| Name | Value | |
|---|---|---|
"PlotType" | A character vector specifying the plot
type. "pdf" plots the probability density function (PDF).
"cdf" plots the cumulative density function (CDF). | |
"Discrete" | A logical scalar to specify whether to
plot the PDF or CDF of a discrete distribution object as a line plot or a
stem plot, by specifying false or true, respectively. By
default, it is true for discrete distributions and false
for continuous distributions. When pd is a continuous distribution
object, this option is ignored. | |
"Parent" | An axes graphics object for the plot. If
not specified, the plot function plots into the current axes or
creates a new axes object if one does not exist. |
h = plot (…) returns a graphics handle to the plotted
objects.
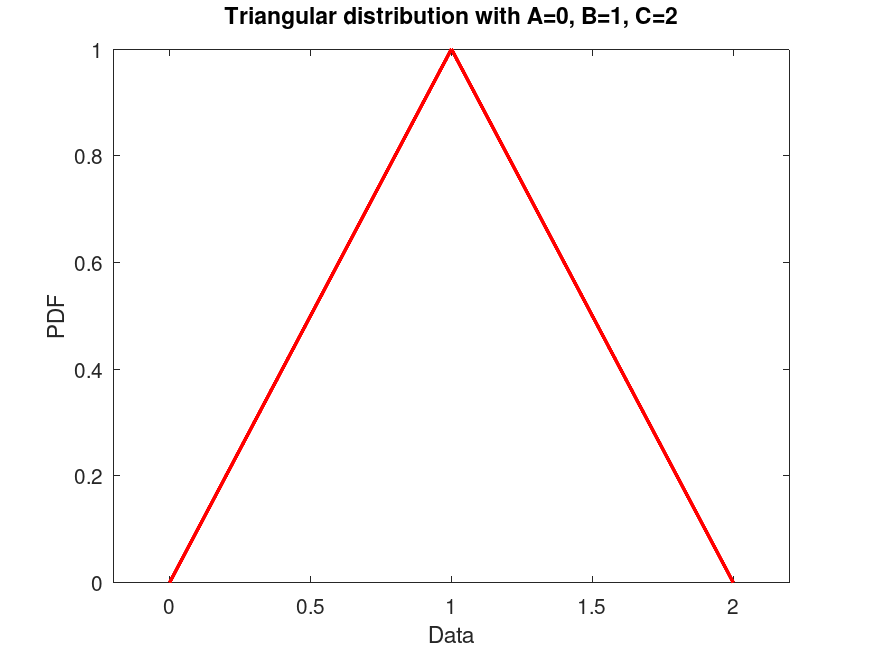
Example: 1
## Create a Triangular distribution with fixed parameters A=0, B=1, C=2
## and plot its PDF.
pd = TriangularDistribution (0, 1, 2);
plot (pd)
title ("Triangular distribution with A=0, B=1, C=2")
## Use this to visualize the PDF of a Triangular distribution with fixed
## parameters, useful for understanding the shape of the distribution.
|
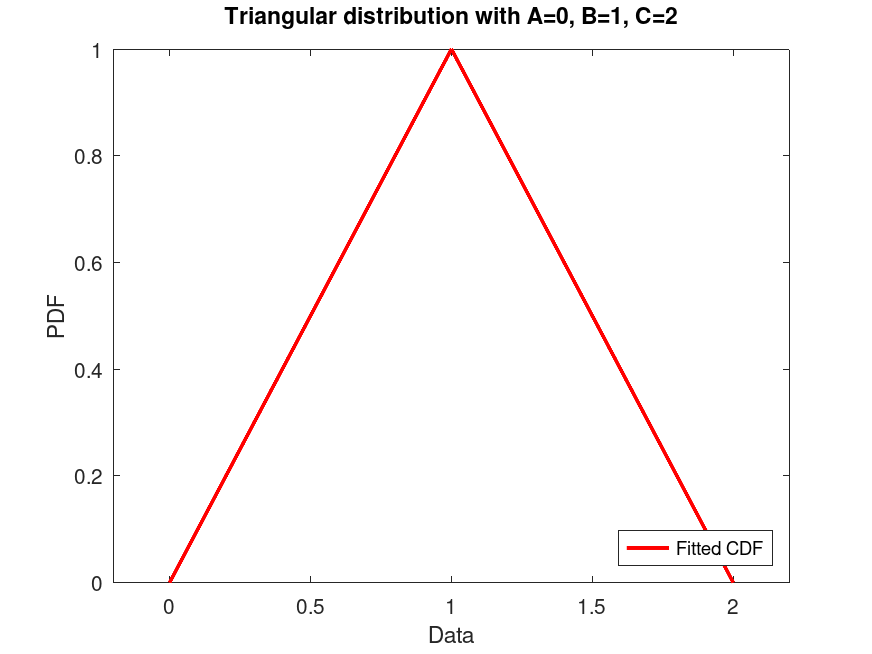
Example: 2
## Generate a data set of 100 random samples from a Triangular distribution
## with parameters A=0, B=1, C=2. Plot its CDF.
rand ("seed", 21);
data = trirnd (0, 1, 2, 100, 1);
pd = makedist ("Triangular", "A", 0, "B", 1, "C", 2);
plot (pd, "PlotType", "cdf")
title ("Triangular distribution with A=0, B=1, C=2")
legend ({"Fitted CDF"}, "location", "southeast")
## Use this to visualize the CDF of a Triangular distribution, useful for
## assessing cumulative probabilities in bounded data scenarios.
|
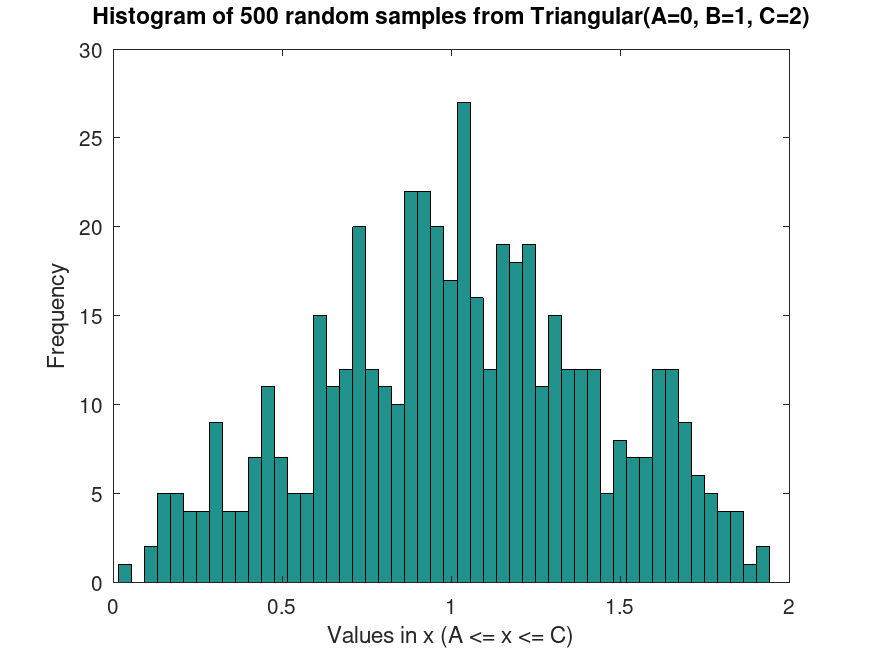
TriangularDistribution: r = random (pd)
TriangularDistribution: r = random (pd, rows)
TriangularDistribution: r = random (pd, rows, cols, …)
TriangularDistribution: r = random (pd, [sz])
r = random (pd) returns a random number from the
distribution object pd.
When called with a single size argument, trirnd returns a square
matrix with the dimension specified. When called with more than one
scalar argument, the first two arguments are taken as the number of rows
and columns and any further arguments specify additional matrix
dimensions. The size may also be specified with a row vector of
dimensions, sz.
Example: 1
## Generate random samples from a Triangular distribution
rand ("seed", 21);
samples = trirnd (0, 1, 2, 500, 1);
hist (samples, 50)
title ("Histogram of 500 random samples from Triangular(A=0, B=1, C=2)")
xlabel ("Values in x (A <= x <= C)")
ylabel ("Frequency")
## This generates random samples from a Triangular distribution, useful for
## simulating bounded data like project costs or completion times.
|
TriangularDistribution: s = std (pd)
s = std (pd) computes the standard deviation of the
probability distribution object, pd.
Example: 1
## Compute the standard deviation for a Triangular distribution
pd = TriangularDistribution (0, 1, 2);
std_value = std (pd)
## Use this to calculate the standard deviation, which measures the variability
## within the bounds of the Triangular distribution, useful for risk assessment.
std_value = 0.4082
|
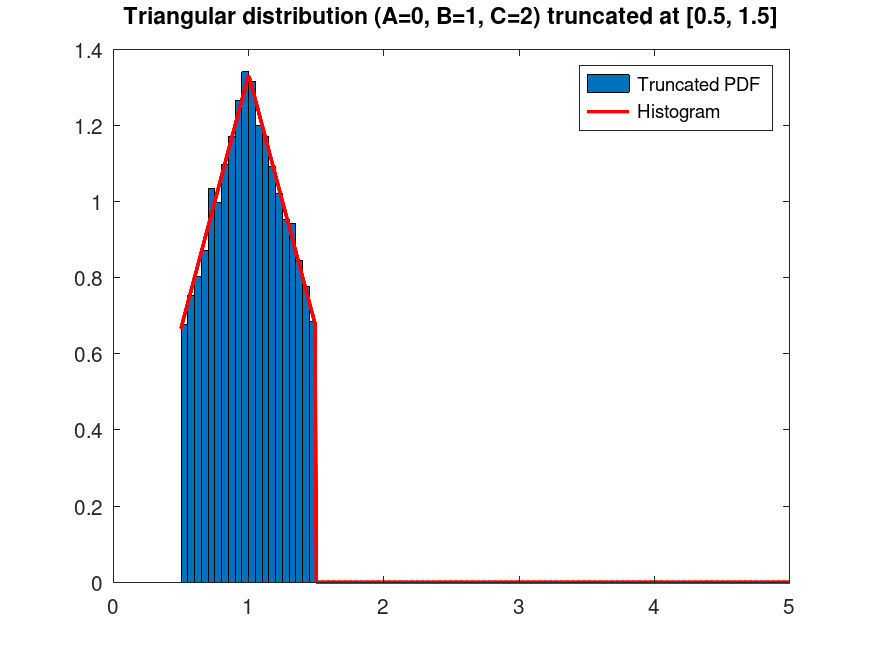
TriangularDistribution: t = truncate (pd, lower, upper)
t = truncate (pd, lower, upper) returns a
probability distribution t, which is the probability distribution
pd truncated to the specified interval with lower limit,
lower, and upper limit, upper.
Example: 1
## Plot the PDF of a Triangular distribution with parameters A=0, B=1, C=2,
## truncated at [0.5, 1.5] intervals. Generate 10000 random samples from this
## truncated distribution and superimpose a histogram scaled accordingly.
rand ("seed", 21);
data_all = trirnd (0, 1, 2, 20000, 1);
data = data_all(data_all >= 0.5 & data_all <= 1.5);
data = data(1:10000);
pd = makedist ("Triangular", "A", 0, "B", 1, "C", 2);
t = truncate (pd, 0.5, 1.5);
[counts, centers] = hist (data, 20);
bin_width = centers(2) - centers(1);
bar (centers, counts / (sum (counts) * bin_width), 1);
hold on;
## Plot histogram and truncated PDF
x = linspace (0.5, 5, 500);
y = pdf (t, x);
plot (x, y, "r", "linewidth", 2);
title ("Triangular distribution (A=0, B=1, C=2) truncated at [0.5, 1.5]")
legend ("Truncated PDF", "Histogram")
## This demonstrates truncating a Triangular distribution to a specific range
## and visualizing the resulting distribution with random samples, useful for
## constrained scenarios like limited budgets.
|
TriangularDistribution: v = var (pd)
v = var (pd) computes the variance of the
probability distribution object, pd.
Example: 1
## Compute the variance for a Triangular distribution
pd = TriangularDistribution (0, 1, 2);
var_value = var (pd)
## Use this to calculate the variance, which quantifies the spread of values
## within the bounds of the Triangular distribution, useful for uncertainty analysis.
var_value = 0.1667
|
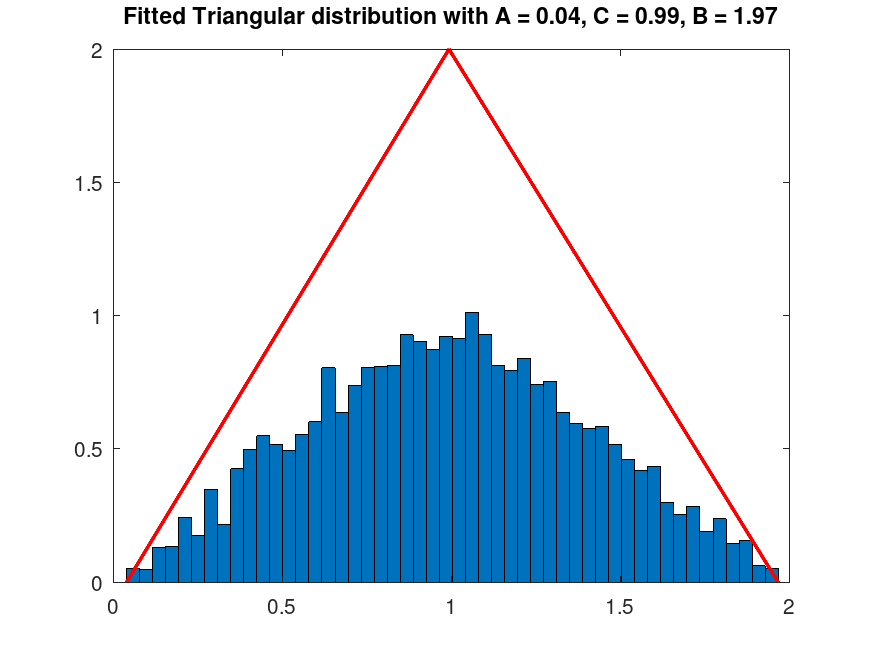
Examples
pd_fixed = makedist ("Triangular", "A", 0, "B", 1, "C", 2);
rand ("seed", 2);
data = random (pd_fixed, 5000, 1);
A = min (data);
C = mean (data);
B = max (data);
[counts, centers] = hist (data, 50);
bin_width = centers(2) - centers(1);
normalized_counts = counts / (sum (counts) * bin_width);
bar (centers, normalized_counts, 1);
hold on;
x = linspace (A, B, 100);
y = (2 * (x - A) / (C - A) .* (x <= C)) + (2 * (B - x) / (B - C) .* (x > C));
plot (x, y, 'r-', 'LineWidth', 2);
msg = sprintf ("Fitted Triangular distribution with A = %0.2f, C = %0.2f, B = %0.2f", A, C, B);
title (msg);
hold off; |