Categories &
Functions List
- BetaDistribution
- BinomialDistribution
- BirnbaumSaundersDistribution
- BurrDistribution
- ExponentialDistribution
- ExtremeValueDistribution
- GammaDistribution
- GeneralizedExtremeValueDistribution
- GeneralizedParetoDistribution
- HalfNormalDistribution
- InverseGaussianDistribution
- LogisticDistribution
- LoglogisticDistribution
- LognormalDistribution
- LoguniformDistribution
- MultinomialDistribution
- NakagamiDistribution
- NegativeBinomialDistribution
- NormalDistribution
- PiecewiseLinearDistribution
- PoissonDistribution
- RayleighDistribution
- RicianDistribution
- tLocationScaleDistribution
- TriangularDistribution
- UniformDistribution
- WeibullDistribution
- betafit
- betalike
- binofit
- binolike
- bisafit
- bisalike
- burrfit
- burrlike
- evfit
- evlike
- expfit
- explike
- gamfit
- gamlike
- geofit
- gevfit_lmom
- gevfit
- gevlike
- gpfit
- gplike
- gumbelfit
- gumbellike
- hnfit
- hnlike
- invgfit
- invglike
- logifit
- logilike
- loglfit
- logllike
- lognfit
- lognlike
- nakafit
- nakalike
- nbinfit
- nbinlike
- normfit
- normlike
- poissfit
- poisslike
- raylfit
- rayllike
- ricefit
- ricelike
- tlsfit
- tlslike
- unidfit
- unifit
- wblfit
- wbllike
- betacdf
- betainv
- betapdf
- betarnd
- binocdf
- binoinv
- binopdf
- binornd
- bisacdf
- bisainv
- bisapdf
- bisarnd
- burrcdf
- burrinv
- burrpdf
- burrrnd
- bvncdf
- bvtcdf
- cauchycdf
- cauchyinv
- cauchypdf
- cauchyrnd
- chi2cdf
- chi2inv
- chi2pdf
- chi2rnd
- copulacdf
- copulapdf
- copularnd
- evcdf
- evinv
- evpdf
- evrnd
- expcdf
- expinv
- exppdf
- exprnd
- fcdf
- finv
- fpdf
- frnd
- gamcdf
- gaminv
- gampdf
- gamrnd
- geocdf
- geoinv
- geopdf
- geornd
- gevcdf
- gevinv
- gevpdf
- gevrnd
- gpcdf
- gpinv
- gppdf
- gprnd
- gumbelcdf
- gumbelinv
- gumbelpdf
- gumbelrnd
- hncdf
- hninv
- hnpdf
- hnrnd
- hygecdf
- hygeinv
- hygepdf
- hygernd
- invgcdf
- invginv
- invgpdf
- invgrnd
- iwishpdf
- iwishrnd
- jsucdf
- jsupdf
- laplacecdf
- laplaceinv
- laplacepdf
- laplacernd
- logicdf
- logiinv
- logipdf
- logirnd
- loglcdf
- loglinv
- loglpdf
- loglrnd
- logncdf
- logninv
- lognpdf
- lognrnd
- mnpdf
- mnrnd
- mvncdf
- mvnpdf
- mvnrnd
- mvtcdf
- mvtpdf
- mvtrnd
- mvtcdfqmc
- nakacdf
- nakainv
- nakapdf
- nakarnd
- nbincdf
- nbininv
- nbinpdf
- nbinrnd
- ncfcdf
- ncfinv
- ncfpdf
- ncfrnd
- nctcdf
- nctinv
- nctpdf
- nctrnd
- ncx2cdf
- ncx2inv
- ncx2pdf
- ncx2rnd
- normcdf
- norminv
- normpdf
- normrnd
- plcdf
- plinv
- plpdf
- plrnd
- poisscdf
- poissinv
- poisspdf
- poissrnd
- raylcdf
- raylinv
- raylpdf
- raylrnd
- ricecdf
- riceinv
- ricepdf
- ricernd
- tcdf
- tinv
- tpdf
- trnd
- tlscdf
- tlsinv
- tlspdf
- tlsrnd
- tricdf
- triinv
- tripdf
- trirnd
- unidcdf
- unidinv
- unidpdf
- unidrnd
- unifcdf
- unifinv
- unifpdf
- unifrnd
- vmcdf
- vminv
- vmpdf
- vmrnd
- wblcdf
- wblinv
- wblpdf
- wblrnd
- wienrnd
- wishpdf
- wishrnd
- adtest
- anova1
- anova2
- anovan
- bartlett_test
- barttest
- binotest
- chi2gof
- chi2test
- correlation_test
- fishertest
- friedman
- hotelling_t2test
- hotelling_t2test2
- kruskalwallis
- kstest
- kstest2
- levene_test
- manova1
- mcnemar_test
- multcompare
- ranksum
- regression_ftest
- regression_ttest
- runstest
- sampsizepwr
- signrank
- signtest
- tiedrank
- ttest
- ttest2
- vartest
- vartest2
- vartestn
- ztest
- ztest2
Function Reference: vartestn
statistics: vartestn (x)
statistics: vartestn (x, group)
statistics: vartestn (…, name, value)
statistics: p = vartestn (…)
statistics: [p, stats] = vartestn (…)
statistics: [p, stats] = vartestn (…, name, value)
Test for equal variances across multiple groups.
h = vartestn (x) performs Bartlett’s test for equal
variances for the columns of the matrix x. This is a test of the null
hypothesis that the columns of x come from normal distributions with
the same variance, against the alternative that they come from normal
distributions with different variances. The result is displayed in a summary
table of statistics as well as a box plot of the groups.
vartestn (x, group) requires a vector x, and a
group argument that is a categorical variable, vector, string array, or
cell array of strings with one row for each element of x. Values of
x corresponding to the same value of group are placed in the same
group.
vartestn treats NaNs as missing values, and ignores them.
p = vartestn (…) returns the probability of observing the
given result, or one more extreme, by chance under the null hypothesis that
all groups have equal variances. Small values of p cast doubt on the
validity of the null hypothesis.
[p, stats] = vartestn (…) returns a structure with
the following fields:
chistat | – the value of the test statistic | |
df | – the degrees of freedom of the test |
[p, stats] = vartestn (…, name, value)
specifies one or more of the following name/value pairs:
"display" | "on" to display a boxplot and table, or
"off" to omit these displays. Default "on". |
"testtype" | One of the following strings to control the type of test to perform |
"Bartlett" | Bartlett’s test (default). | |
"LeveneQuadratic" | Levene’s test computed by performing anova on the squared deviations of the data values from their group means. | |
"LeveneAbsolute" | Levene’s test computed by performing anova on the absolute deviations of the data values from their group means. | |
"BrownForsythe" | Brown-Forsythe test computed by performing anova on the absolute deviations of the data values from the group medians. | |
"OBrien" | O’Brien’s modification of Levene’s test with . |
The classical Bartlett’s test is sensitive to the assumption that the
distribution in each group is normal. The other test types are more robust
to non-normal distributions, especially ones prone to outliers. For these
tests, the STATS output structure has a field named fstat containing
the test statistic, and df1 and df2 containing its numerator
and denominator degrees of freedom.
See also: vartest, vartest2, anova1, bartlett_test, levene_test
Source Code: vartestn
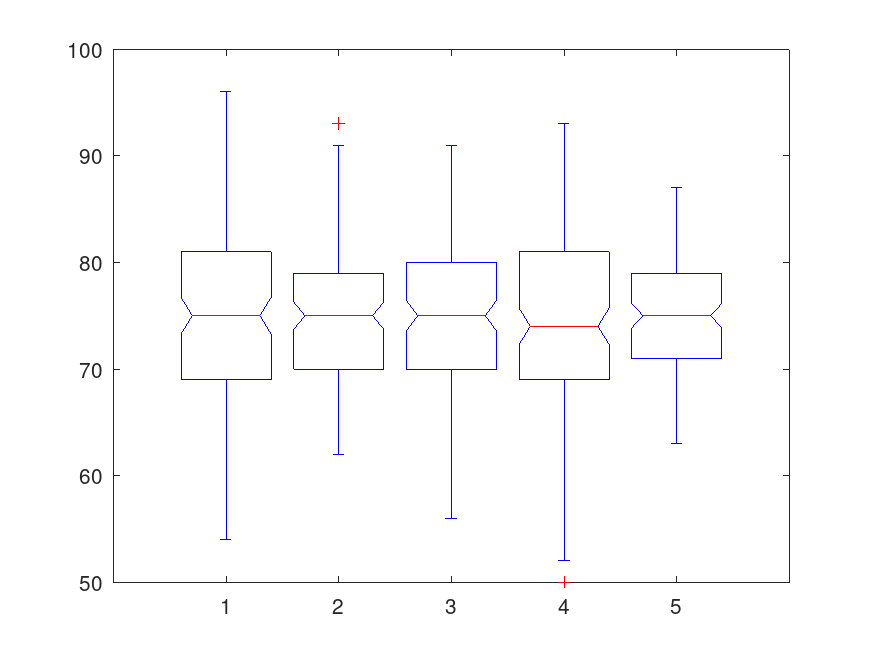
Example: 1
## Test the null hypothesis that the variances are equal across the five
## columns of data in the students’ exam grades matrix, grades.
load examgrades
vartestn (grades)
Group Summary Table
Group Count Mean Std Dev
------------------------------------------------------------
1 120 75.0083 8.720203
2 120 74.9917 6.542037
3 120 74.9917 7.430910
4 120 75.0333 8.601283
5 120 74.9917 5.258839
Pooled Groups 600 75.0033 7.310655
Pooled valid Groups 600 75.0083 8.720203
Bartlett's statistic 38.73324
Degrees of Freedom 4
p-value 0.000000
ans = 7.9086e-08
|
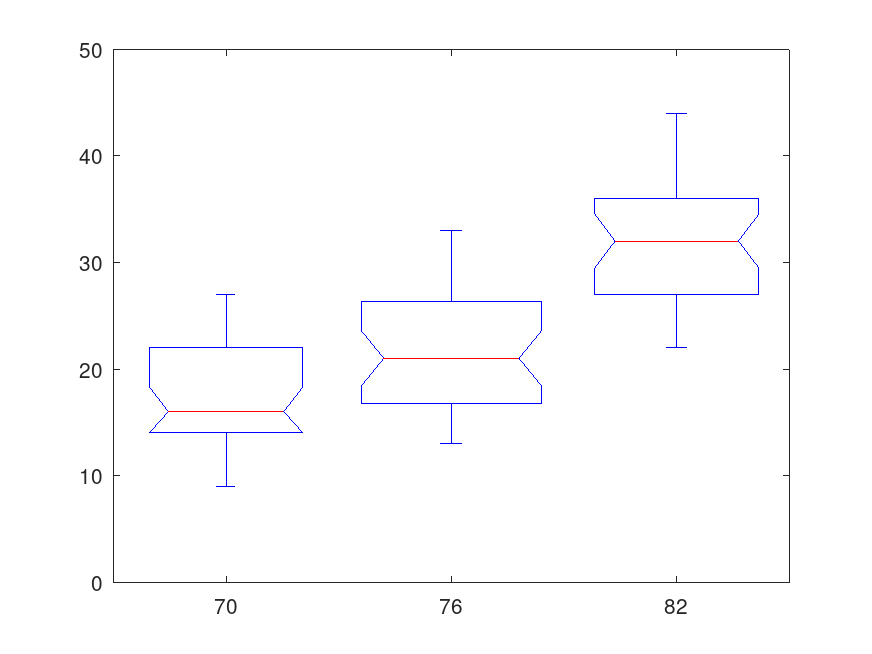
Example: 2
## Test the null hypothesis that the variances in miles per gallon (MPG) are
## equal across different model years.
load carsmall
vartestn (MPG, Model_Year)
Group Summary Table
Group Count Mean Std Dev
------------------------------------------------------------
70 29 17.6897 5.339231
76 34 21.5735 5.889297
82 31 31.7097 5.392548
Pooled Groups 94 23.6576 5.540359
Pooled valid Groups 87 17.6897 5.339231
Bartlett's statistic 0.36619
Degrees of Freedom 2
p-value 0.832687
ans = 0.8327
|
Example: 3
## Use Levene’s test to test the null hypothesis that the variances in miles
## per gallon (MPG) are equal across different model years.
load carsmall
p = vartestn (MPG, Model_Year, "TestType", "LeveneAbsolute")
Group Summary Table
Group Count Mean Std Dev
------------------------------------------------------------
70 29 17.6897 5.339231
76 34 21.5735 5.889297
82 31 31.7097 5.392548
Pooled Groups 94 23.6576 5.540359
Pooled valid Groups 2958 23.7181 5.555774
Levene's statistic (absolute) 0.46126
Degrees of Freedom 2, 91
p-value 0.631954
p = 0.6320
|
Example: 4
## Test the null hypothesis that the variances are equal across the five
## columns of data in the students’ exam grades matrix, grades, using the
## Brown-Forsythe test. Suppress the display of the summary table of
## statistics and the box plot.
load examgrades
[p, stats] = vartestn (grades, "TestType", "BrownForsythe", "Display", "off")
p = 1.3121e-06
stats =
scalar structure containing the fields:
fstat = 8.4160
df =
4 595
|