Categories &
Functions List
- BetaDistribution
- BinomialDistribution
- BirnbaumSaundersDistribution
- BurrDistribution
- ExponentialDistribution
- ExtremeValueDistribution
- GammaDistribution
- GeneralizedExtremeValueDistribution
- GeneralizedParetoDistribution
- HalfNormalDistribution
- InverseGaussianDistribution
- LogisticDistribution
- LoglogisticDistribution
- LognormalDistribution
- LoguniformDistribution
- MultinomialDistribution
- NakagamiDistribution
- NegativeBinomialDistribution
- NormalDistribution
- PiecewiseLinearDistribution
- PoissonDistribution
- RayleighDistribution
- RicianDistribution
- tLocationScaleDistribution
- TriangularDistribution
- UniformDistribution
- WeibullDistribution
- betafit
- betalike
- binofit
- binolike
- bisafit
- bisalike
- burrfit
- burrlike
- evfit
- evlike
- expfit
- explike
- gamfit
- gamlike
- geofit
- gevfit_lmom
- gevfit
- gevlike
- gpfit
- gplike
- gumbelfit
- gumbellike
- hnfit
- hnlike
- invgfit
- invglike
- logifit
- logilike
- loglfit
- logllike
- lognfit
- lognlike
- nakafit
- nakalike
- nbinfit
- nbinlike
- normfit
- normlike
- poissfit
- poisslike
- raylfit
- rayllike
- ricefit
- ricelike
- tlsfit
- tlslike
- unidfit
- unifit
- wblfit
- wbllike
- betacdf
- betainv
- betapdf
- betarnd
- binocdf
- binoinv
- binopdf
- binornd
- bisacdf
- bisainv
- bisapdf
- bisarnd
- burrcdf
- burrinv
- burrpdf
- burrrnd
- bvncdf
- bvtcdf
- cauchycdf
- cauchyinv
- cauchypdf
- cauchyrnd
- chi2cdf
- chi2inv
- chi2pdf
- chi2rnd
- copulacdf
- copulapdf
- copularnd
- evcdf
- evinv
- evpdf
- evrnd
- expcdf
- expinv
- exppdf
- exprnd
- fcdf
- finv
- fpdf
- frnd
- gamcdf
- gaminv
- gampdf
- gamrnd
- geocdf
- geoinv
- geopdf
- geornd
- gevcdf
- gevinv
- gevpdf
- gevrnd
- gpcdf
- gpinv
- gppdf
- gprnd
- gumbelcdf
- gumbelinv
- gumbelpdf
- gumbelrnd
- hncdf
- hninv
- hnpdf
- hnrnd
- hygecdf
- hygeinv
- hygepdf
- hygernd
- invgcdf
- invginv
- invgpdf
- invgrnd
- iwishpdf
- iwishrnd
- jsucdf
- jsupdf
- laplacecdf
- laplaceinv
- laplacepdf
- laplacernd
- logicdf
- logiinv
- logipdf
- logirnd
- loglcdf
- loglinv
- loglpdf
- loglrnd
- logncdf
- logninv
- lognpdf
- lognrnd
- mnpdf
- mnrnd
- mvncdf
- mvnpdf
- mvnrnd
- mvtcdf
- mvtpdf
- mvtrnd
- mvtcdfqmc
- nakacdf
- nakainv
- nakapdf
- nakarnd
- nbincdf
- nbininv
- nbinpdf
- nbinrnd
- ncfcdf
- ncfinv
- ncfpdf
- ncfrnd
- nctcdf
- nctinv
- nctpdf
- nctrnd
- ncx2cdf
- ncx2inv
- ncx2pdf
- ncx2rnd
- normcdf
- norminv
- normpdf
- normrnd
- plcdf
- plinv
- plpdf
- plrnd
- poisscdf
- poissinv
- poisspdf
- poissrnd
- raylcdf
- raylinv
- raylpdf
- raylrnd
- ricecdf
- riceinv
- ricepdf
- ricernd
- tcdf
- tinv
- tpdf
- trnd
- tlscdf
- tlsinv
- tlspdf
- tlsrnd
- tricdf
- triinv
- tripdf
- trirnd
- unidcdf
- unidinv
- unidpdf
- unidrnd
- unifcdf
- unifinv
- unifpdf
- unifrnd
- vmcdf
- vminv
- vmpdf
- vmrnd
- wblcdf
- wblinv
- wblpdf
- wblrnd
- wienrnd
- wishpdf
- wishrnd
- adtest
- anova1
- anova2
- anovan
- bartlett_test
- barttest
- binotest
- chi2gof
- chi2test
- correlation_test
- fishertest
- friedman
- hotelling_t2test
- hotelling_t2test2
- kruskalwallis
- kstest
- kstest2
- levene_test
- manova1
- mcnemar_test
- multcompare
- ranksum
- regression_ftest
- regression_ttest
- runstest
- sampsizepwr
- signrank
- signtest
- tiedrank
- ttest
- ttest2
- vartest
- vartest2
- vartestn
- ztest
- ztest2
Function Reference: invgfit
statistics: paramhat = invgfit (x)
statistics: [paramhat, paramci] = invgfit (x)
statistics: [paramhat, paramci] = invgfit (x, alpha)
statistics: […] = invgfit (x, alpha, censor)
statistics: […] = invgfit (x, alpha, censor, freq)
statistics: […] = invgfit (x, alpha, censor, freq, options)
Estimate mean and confidence intervals for the inverse Gaussian distribution.
mu0 = invgfit (x) returns the maximum likelihood
estimates of the parameters of the inverse Gaussian distribution given the
data in x. paramhat(1) is the scale parameter, mu,
and paramhat(2) is the shape parameter, lambda.
[paramhat, paramci] = invgfit (x) returns the 95%
confidence intervals for the parameter estimates.
[…] = invgfit (x, alpha) also returns the
100 * (1 - alpha) percent confidence intervals for the
parameter estimates. By default, the optional argument alpha is
0.05 corresponding to 95% confidence intervals. Pass in [] for
alpha to use the default values.
[…] = invgfit (x, alpha, censor) accepts a
boolean vector, censor, of the same size as x with 1s for
observations that are right-censored and 0s for observations that are
observed exactly. By default, or if left empty,
censor = zeros (size (x)).
[…] = invgfit (x, alpha, censor, freq)
accepts a frequency vector, freq, of the same size as x.
freq typically contains integer frequencies for the corresponding
elements in x, but it can contain any non-integer non-negative values.
By default, or if left empty, freq = ones (size (x)).
[…] = invgfit (…, options) specifies control
parameters for the iterative algorithm used to compute ML estimates with the
fminsearch function. options is a structure with the following
fields and their default values:
-
options.Display = "off" -
options.MaxFunEvals = 400 -
options.MaxIter = 200 -
options.TolX = 1e-6
Further information about the inverse Gaussian distribution can be found at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inverse_Gaussian_distribution
See also: invgcdf, invginv, invgpdf, invgrnd, invglike, invgstat
Source Code: invgfit
Example: 1
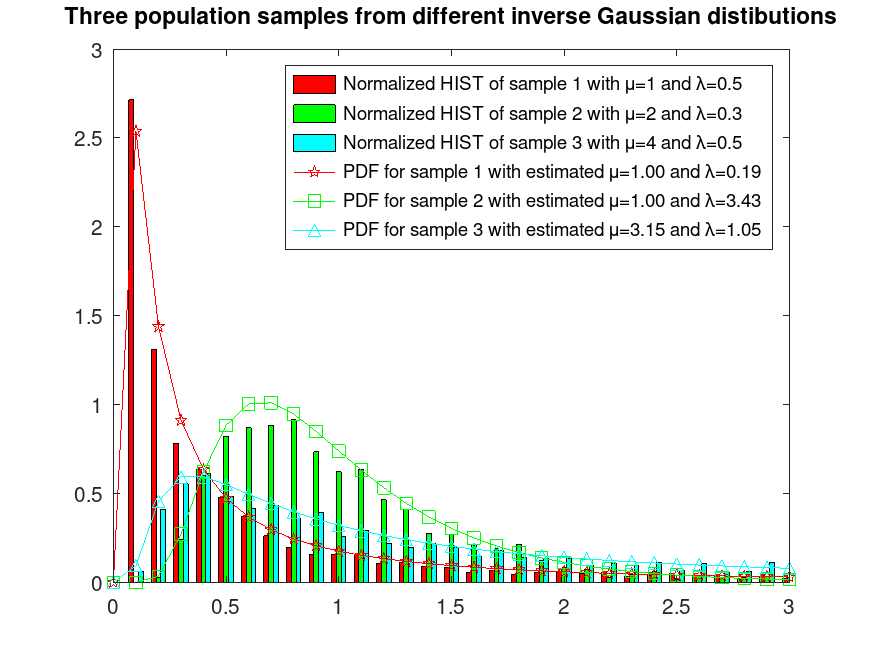
## Sample 3 populations from different inverse Gaussian distributions
rand ("seed", 5); randn ("seed", 5); # for reproducibility
r1 = invgrnd (1, 0.2, 2000, 1);
rand ("seed", 2); randn ("seed", 2); # for reproducibility
r2 = invgrnd (1, 3, 2000, 1);
rand ("seed", 7); randn ("seed", 7); # for reproducibility
r3 = invgrnd (3, 1, 2000, 1);
r = [r1, r2, r3];
## Plot them normalized and fix their colors
hist (r, [0.1:0.1:3.2], 9);
h = findobj (gca, "Type", "patch");
set (h(1), "facecolor", "c");
set (h(2), "facecolor", "g");
set (h(3), "facecolor", "r");
ylim ([0, 3]);
xlim ([0, 3]);
hold on
## Estimate their MU and LAMBDA parameters
mu_lambdaA = invgfit (r(:,1));
mu_lambdaB = invgfit (r(:,2));
mu_lambdaC = invgfit (r(:,3));
## Plot their estimated PDFs
x = [0:0.1:3];
y = invgpdf (x, mu_lambdaA(1), mu_lambdaA(2));
plot (x, y, "-pr");
y = invgpdf (x, mu_lambdaB(1), mu_lambdaB(2));
plot (x, y, "-sg");
y = invgpdf (x, mu_lambdaC(1), mu_lambdaC(2));
plot (x, y, "-^c");
hold off
legend ({"Normalized HIST of sample 1 with μ=1 and λ=0.5", ...
"Normalized HIST of sample 2 with μ=2 and λ=0.3", ...
"Normalized HIST of sample 3 with μ=4 and λ=0.5", ...
sprintf("PDF for sample 1 with estimated μ=%0.2f and λ=%0.2f", ...
mu_lambdaA(1), mu_lambdaA(2)), ...
sprintf("PDF for sample 2 with estimated μ=%0.2f and λ=%0.2f", ...
mu_lambdaB(1), mu_lambdaB(2)), ...
sprintf("PDF for sample 3 with estimated μ=%0.2f and λ=%0.2f", ...
mu_lambdaC(1), mu_lambdaC(2))})
title ("Three population samples from different inverse Gaussian distributions")
hold off
|