Categories &
Functions List
- BetaDistribution
- BinomialDistribution
- BirnbaumSaundersDistribution
- BurrDistribution
- ExponentialDistribution
- ExtremeValueDistribution
- GammaDistribution
- GeneralizedExtremeValueDistribution
- GeneralizedParetoDistribution
- HalfNormalDistribution
- InverseGaussianDistribution
- LogisticDistribution
- LoglogisticDistribution
- LognormalDistribution
- LoguniformDistribution
- MultinomialDistribution
- NakagamiDistribution
- NegativeBinomialDistribution
- NormalDistribution
- PiecewiseLinearDistribution
- PoissonDistribution
- RayleighDistribution
- RicianDistribution
- tLocationScaleDistribution
- TriangularDistribution
- UniformDistribution
- WeibullDistribution
- betafit
- betalike
- binofit
- binolike
- bisafit
- bisalike
- burrfit
- burrlike
- evfit
- evlike
- expfit
- explike
- gamfit
- gamlike
- geofit
- gevfit_lmom
- gevfit
- gevlike
- gpfit
- gplike
- gumbelfit
- gumbellike
- hnfit
- hnlike
- invgfit
- invglike
- logifit
- logilike
- loglfit
- logllike
- lognfit
- lognlike
- nakafit
- nakalike
- nbinfit
- nbinlike
- normfit
- normlike
- poissfit
- poisslike
- raylfit
- rayllike
- ricefit
- ricelike
- tlsfit
- tlslike
- unidfit
- unifit
- wblfit
- wbllike
- betacdf
- betainv
- betapdf
- betarnd
- binocdf
- binoinv
- binopdf
- binornd
- bisacdf
- bisainv
- bisapdf
- bisarnd
- burrcdf
- burrinv
- burrpdf
- burrrnd
- bvncdf
- bvtcdf
- cauchycdf
- cauchyinv
- cauchypdf
- cauchyrnd
- chi2cdf
- chi2inv
- chi2pdf
- chi2rnd
- copulacdf
- copulapdf
- copularnd
- evcdf
- evinv
- evpdf
- evrnd
- expcdf
- expinv
- exppdf
- exprnd
- fcdf
- finv
- fpdf
- frnd
- gamcdf
- gaminv
- gampdf
- gamrnd
- geocdf
- geoinv
- geopdf
- geornd
- gevcdf
- gevinv
- gevpdf
- gevrnd
- gpcdf
- gpinv
- gppdf
- gprnd
- gumbelcdf
- gumbelinv
- gumbelpdf
- gumbelrnd
- hncdf
- hninv
- hnpdf
- hnrnd
- hygecdf
- hygeinv
- hygepdf
- hygernd
- invgcdf
- invginv
- invgpdf
- invgrnd
- iwishpdf
- iwishrnd
- jsucdf
- jsupdf
- laplacecdf
- laplaceinv
- laplacepdf
- laplacernd
- logicdf
- logiinv
- logipdf
- logirnd
- loglcdf
- loglinv
- loglpdf
- loglrnd
- logncdf
- logninv
- lognpdf
- lognrnd
- mnpdf
- mnrnd
- mvncdf
- mvnpdf
- mvnrnd
- mvtcdf
- mvtpdf
- mvtrnd
- mvtcdfqmc
- nakacdf
- nakainv
- nakapdf
- nakarnd
- nbincdf
- nbininv
- nbinpdf
- nbinrnd
- ncfcdf
- ncfinv
- ncfpdf
- ncfrnd
- nctcdf
- nctinv
- nctpdf
- nctrnd
- ncx2cdf
- ncx2inv
- ncx2pdf
- ncx2rnd
- normcdf
- norminv
- normpdf
- normrnd
- plcdf
- plinv
- plpdf
- plrnd
- poisscdf
- poissinv
- poisspdf
- poissrnd
- raylcdf
- raylinv
- raylpdf
- raylrnd
- ricecdf
- riceinv
- ricepdf
- ricernd
- tcdf
- tinv
- tpdf
- trnd
- tlscdf
- tlsinv
- tlspdf
- tlsrnd
- tricdf
- triinv
- tripdf
- trirnd
- unidcdf
- unidinv
- unidpdf
- unidrnd
- unifcdf
- unifinv
- unifpdf
- unifrnd
- vmcdf
- vminv
- vmpdf
- vmrnd
- wblcdf
- wblinv
- wblpdf
- wblrnd
- wienrnd
- wishpdf
- wishrnd
- adtest
- anova1
- anova2
- anovan
- bartlett_test
- barttest
- binotest
- chi2gof
- chi2test
- correlation_test
- fishertest
- friedman
- hotelling_t2test
- hotelling_t2test2
- kruskalwallis
- kstest
- kstest2
- levene_test
- manova1
- mcnemar_test
- multcompare
- ranksum
- regression_ftest
- regression_ttest
- runstest
- sampsizepwr
- signrank
- signtest
- tiedrank
- ttest
- ttest2
- vartest
- vartest2
- vartestn
- ztest
- ztest2
Function Reference: fitgmdist
statistics: GMdist = fitgmdist (data, k, param1, value1, …)
Fit a Gaussian mixture model with k components to data. Each row of data is a data sample. Each column is a variable.
Optional parameters are:
-
"start": Initialization conditions. Possible values are:-
"randSample"(default) Takes means uniformly from rows of data. -
"plus"Use k-means++ to initialize means. -
"cluster"Performs an initial clustering with 10% of the data. - vector A vector whose length is the number of rows in data, and whose values are 1 to k specify the components each row is initially allocated to. The mean, variance, and weight of each component is calculated from that.
- structure A structure with fields
mu,SigmaandComponentProportion.
For
"randSample","plus", and"cluster", the initial variance of each component is the variance of the entire data sample. -
-
"Replicates": Number of random restarts to perform. -
"RegularizationValue"or"Regularize": A small number added to the diagonal entries of the covariance to prevent singular covariances. -
"SharedCovariance"or"SharedCov"(logical). True if all components must share the same variance, to reduce the number of free parameters -
"CovarianceType"or"CovType"(string). Possible values are:-
"full"(default) Allow arbitrary covariance matrices. -
"diagonal"Force covariances to be diagonal, to reduce the number of free parameters.
-
-
"Options": A structure with all of the following fields:-
MaxIterMaximum number of EM iterations (default 100). -
TolFunThreshold increase in likelihood to terminate EM (default 1e-6). -
DisplayPossible values are:-
"off"(default): Display nothing. -
"final": Display the total number of iterations and likelihood once the execution completes. -
"iter": Display the number of iteration and likelihood after each iteration.
-
-
-
"Weight": A column vector or matrix. The first column consists of non-negative weights given to the samples. If these are all integers, this is equivalent to specifyingweight(i)copies of rowiof data, but potentially faster. If a row of data is used to represent samples that are similar but not identical, then the second column of weight indicates the variance of those original samples. Specifically, in the EM algorithm, the contribution of rowitowards the variance is set to at leastweight(i,2), to prevent spurious components with zero variance.
See also: gmdistribution, kmeans
Source Code: fitgmdist
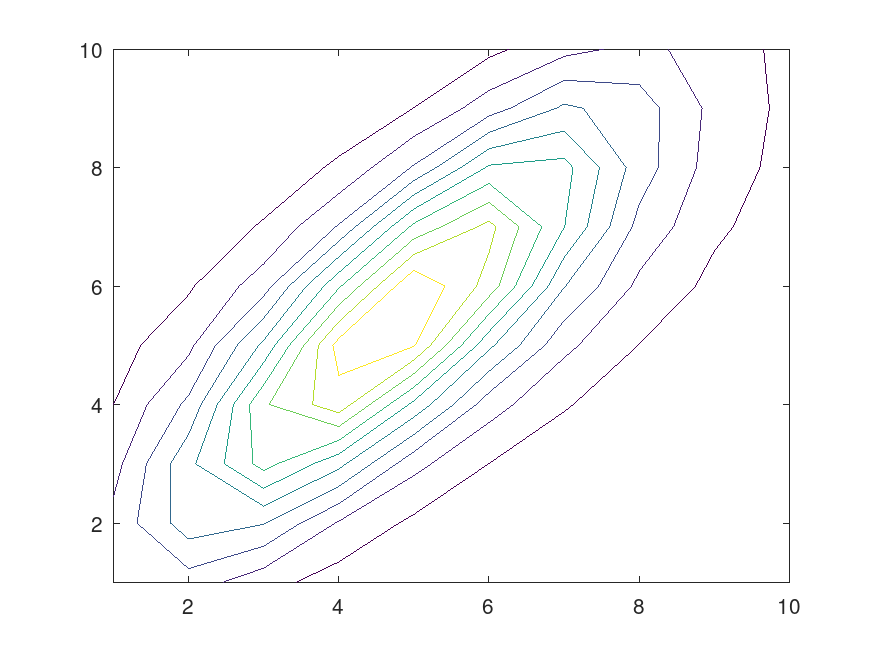
Example: 1
## Generate a two-cluster problem
C1 = randn (100, 2) + 2;
C2 = randn (100, 2) - 2;
data = [C1; C2];
## Perform clustering
GMModel = fitgmdist (data, 2);
## Plot the result
figure
[heights, bins] = hist3([C1; C2]);
[xx, yy] = meshgrid(bins{1}, bins{2});
bbins = [xx(:), yy(:)];
contour (reshape (GMModel.pdf (bbins), size (heights)));
|
Example: 2
Angle_Theta = [ 30 + 10 * randn(1, 10), 60 + 10 * randn(1, 10) ]';
nbOrientations = 2;
initial_orientations = [38.0; 18.0];
initial_weights = ones (1, nbOrientations) / nbOrientations;
initial_Sigma = 10 * ones (1, 1, nbOrientations);
start = struct ("mu", initial_orientations, "Sigma", initial_Sigma, ...
"ComponentProportion", initial_weights);
GMModel_Theta = fitgmdist (Angle_Theta, nbOrientations, "Start", start , ...
"RegularizationValue", 0.0001)
Gaussian mixture distribution with 2 components in 1 dimension(s)
Clust 1: weight 0.701113
Mean: 50.5551
Variance:135.42
Clust 2: weight 0.298887
Mean: 19.3242
Variance:23.764
AIC=175.832 BIC=180.811 NLogL=82.9162 Iter=10 Cged=1 Reg=0.0001
|